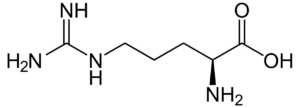
 Arginine
Arginine
Arginine is a conditionally nonessential amino acid, meaning most of the time it can be manufactured by the human body, and does not need to be obtained directly through the diet. The biosynthetic pathway however does not produce sufficient arginine, and some must still be consumed through diet. Individuals who have poor nutrition or certain physical conditions may be advised to increase their intake of foods containing arginine. Arginine is found in a wide variety of foods, including:
* Vegetable sources: wheat germ and flour, buckwheat, granola, oatmeal, nuts (coconut, pecans, cashews, walnuts, almonds, Brazil nuts, hazelnuts, pinenuts, peanuts), seeds (pumpkin, sesame, sunflower), chick peas, cooked soybeans
* Animal sources: dairy products (e.g. cottage cheese, ricotta, milk, yogurt, whey protein drinks), beef, pork (e.g. bacon, ham), poultry (e.g. chicken and turkey light meat), wild game (e.g. pheasant, quail), seafood (e.g. halibut, lobster, salmon, shrimp, snails, tuna)
Arginine has an anti-inflammatoryactivity but also a “rehydrating and normalizing” effect. When combined with glycolic acid delivers all the benefits associated with alphahydroxy acids including exfoliation, increased cell turnover,skin firming and reduced hyperpigmentation. But arginine does this without the stinging, itching and burning often associated with acid resurfacing.





